
Peripheral immune landscape for hypercytokinemia in myasthenic crisis utilizing single-cell transcriptomics - Journal of Translational Medicine
Source : https://translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12967-023-04421-y
Background Myasthenia gravis (MG) is the most prevalent autoimmune disorder affecting the neuromuscular junction. A rapid deterioration in respiratory muscle can lead to a myasthenic crisis (MC), which represents a...
Summary: Our integrated analysis of single-cell transcriptomics and TCR/BCR sequencing has underscored the role of innate immune activation which is associated with hypercytokinemia in MC. The identification of a specific monocyte cluster that dominates the peripheral immune profile may provide some hints into the etiology and pathology of...
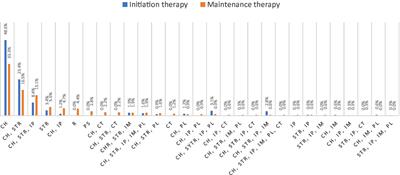
Diagnosis and therapy of myasthenia gravis-the patients' perspective: a cross-sectional study
Source : https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2023.1214041/full
The survey aimed to explore patients' perspectives with myasthenia gravis (MG) toward the diagnosis made and the therapy used to treat MG. The survey was conducted with a quantitative method,...
Conclusion and recommendations: Implementing these recommendations will support a patient-centered approach to managing MG, considering patients’ overall well-being. It will improve treatment outcomes and an enhanced quality of life for individuals with MG.
A decentralized, prospective, observational study to collect real-world data from patients with myasthenia gravis using smartphones
Source : https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2023.1144183/full
IntroductionWe conducted a 3-month, prospective study in a population of patients with Myasthenia Gravis (MG), utilizing a fully decentralized approach for recruitment and monitoring (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04590716).
Conclusion: While these symptom signatures require further study and validation, our results suggest that digital phenotyping, characterized by increased multidimensionality and frequency of the data collection, holds promise for furthering our understanding of clinically significant exacerbations and reimagining the approach to treating MG...

IgG1-3 MuSK Antibodies Inhibit AChR Cluster Formation, Restored by SHP2 Inhibitor, Despite Normal MuSK, DOK7, or AChR Subunit Phosphorylation
Source : https://nn.neurology.org/content/10/6/e200147
Background and Objectives Up to 50% of patients with myasthenia gravis (MG) without acetylcholine receptor antibodies (AChR-Abs) have antibodies to muscle-specific kinase (MuSK). Most MuSK antibodies (MuSK-Abs) are IgG4 and...
Discussion: MuSK-IgG1-3 is pathogenic but seems to act through a noncanonical pathway. Further studies should throw light on the mechanisms involved at the neuromuscular junction.
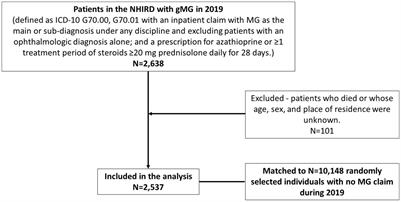
Healthcare resource utilization and costs associated with generalized myasthenia gravis: a retrospective matched cohort study using the National Health Insurance Research Database in Taiwan
Source : https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2023.1216595/full
BackgroundWe estimated healthcare resource utilization (HRU) and costs in patients with generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) in Taiwan.MethodsThis retrospective population-based, matched cohort study used the National Health Insurance Research Database to...
Conclusion: gMG presents a substantial burden on HRU and healthcare costs in Taiwan. A high attrition rate from full-time employment suggests additional societal costs. Improved treatments are needed to alleviate the burden of disease on individuals, healthcare systems, and economies.

