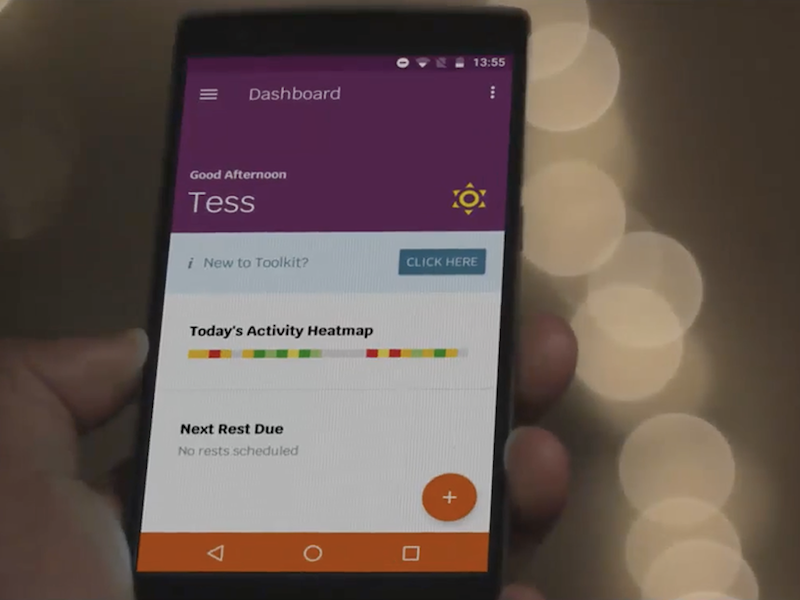
Creating a Digital Toolkit to Reduce Fatigue and Promote Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis: Participatory Design and Usability Study
Source : https://formative.jmir.org/2021/12/e19230/
Background: Fatigue is one of the most common and debilitating symptoms of multiple sclerosis (MS), experienced by more than 80% of people with MS. FACETS (Fatigue: Applying Cognitive Behavioral and...
Conclusions: This work highlights the importance of the participation of people with MS across the entire development cycle, working to a human-centered design methodology to enable a considered and MS-centered solution to be developed. Continued horizon scanning for emergent technological enhancements will enable us to identify opportunities...

Reduced expression of mitochondrial fumarate hydratase in progressive multiple sclerosis contributes to impaired in vitro mesenchymal stromal cell-mediated neuroprotection - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34841955/
Our findings are further evidence of dysregulation of the bone marrow microenvironment in progressive MS with respect to anti-oxidative capacity and immunoregulatory potential. Given the clinical utility of the fumaric...
Conclusions: Our findings are further evidence of dysregulation of the bone marrow microenvironment in progressive MS with respect to anti-oxidative capacity and immunoregulatory potential. Given the clinical utility of the fumaric acid ester dimethyl fumarate in relapsing–remitting MS, our findings have potential implication for...
Functional Connectivity Lateralisation Shift of Resting State Networks is Linked to Visuospatial Memory and White Matter Microstructure in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis - Brain Topography
Source : https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10548-021-00881-x
Laterality patterns of resting state networks (RSN) change in various neuropsychiatric conditions. Multiple sclerosis (MS) causes neuro-cognitive symptoms involving dysfunctional large-scale brain networks. Yet, whether healthy laterality patterns of RSNs...
Diminished dorsal attention network laterality was associated with increased fractional anisotropy asymmetry in the superior longitudinal fasciculus (p
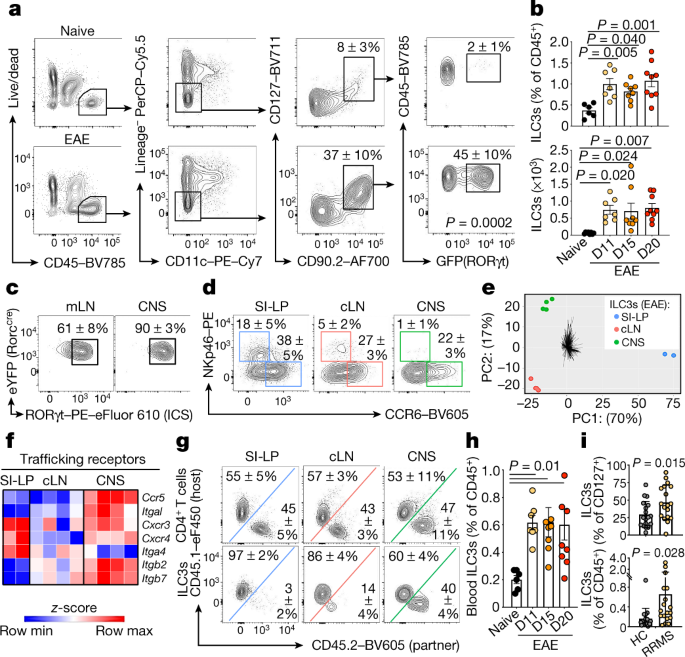
Antigen-presenting innate lymphoid cells orchestrate neuroinflammation - Nature
Source : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-04136-4
Pro-inflammatory T cells in the central nervous system (CNS) are causally associated with multiple demyelinating and neurodegenerative diseases1-6, but the pathways that control these responses remain unclear. Here we define...
Collectively, our data define a population of inflammatory ILC3s that is essential for directly promoting T-cell-dependent neuroinflammation in the CNS and reveal the potential of harnessing peripheral tissue-resident ILC3s for the prevention of autoimmune disease.
Conclusion: The association between NfL and myelin MRI markers suggest that elevated serum NfL is a useful biomarker that reflects not only acute axonal damage, but also damage to myelin and inflammation, likely due to the known synergistic myelin-axon coupling relationship.

