
Myasthenia Gravis and Ischemic Stroke: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37403387/
Bidirectional MR analysis did not provide evidence to support a causal relationship between genetically predicted MG and IS, although observational studies have found such a potential link.
Conclusion: Bidirectional MR analysis did not provide evidence to support a causal relationship between genetically predicted MG and IS, although observational studies have found such a potential link.

Myasthenia gravis and independent risk factors for recurrent infection: a retrospective cohort study - BMC Neurology
Source : https://bmcneurol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12883-023-03306-3
Background Approximately 10% to 20% of myasthenia gravis (MG) patients have experienced a myasthenic crisis (MC), which contributes to morbidity and mortality. MC triggered by infection is associated with poor...
Conclusions: The independent risk factors for recurrent infections in MG patients identified in this study include the presence of concomitant diabetes mellitus, hypomagnesaemia, activated partial thromboplastin time prolongation, and longer duration of hospitalization, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to prevent recurrent...
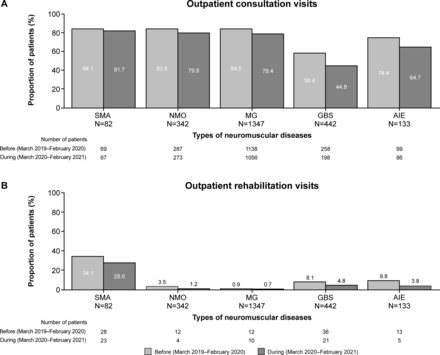
Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on outpatient care and rehabilitation in neuromuscular clinical practice in Japan: a health insurance claims database analysis
Source : https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/13/6/e070818
Objectives To evaluate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on outpatient care in Japanese patients with neuromuscular diseases (NMDs). Design This retrospective cohort study included patients between January 2018 and...
Conclusions: Outpatient consultation and rehabilitation visits during the COVID-19 pandemic were affected in Japanese patients with NMDs. Longer-term evaluations are required to understand if these reductions in outpatient care would affect patient prognosis.

Retracted: miR-181a Ameliorates the Progression of Myasthenia Gravis by Regulating TRIM9
Source : https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2023/9861015/
Retracted: miR-181a Ameliorates the Progression of Myasthenia Gravis by Regulating TRIM9
Relevance: This article has been retracted by Hindawi following an investigation undertaken by the publisher.

Efgartigimod Alfa in Generalised Myasthenia Gravis: A Profile of Its Use - CNS Drugs
Source : https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40263-023-01000-z
Intravenous efgartigimod alfa (also known as efgartigimod alfa-fcab in the USA; Vyvgart®) is the first neonatal Fc receptor antagonist approved in several countries worldwide, including the USA and EU for...
Conclusions/Relevance: The clinical benefits of efgartigimod alfa were durable and reproducible. Furthermore, in an interim analysis of the ongoing open-label phase 3 ADAPT+ extension trial, efgartigimod alfa provided consistent clinically meaningful improvements in patients with gMG. Efgartigimod alfa was generally well tolerated, with most...

