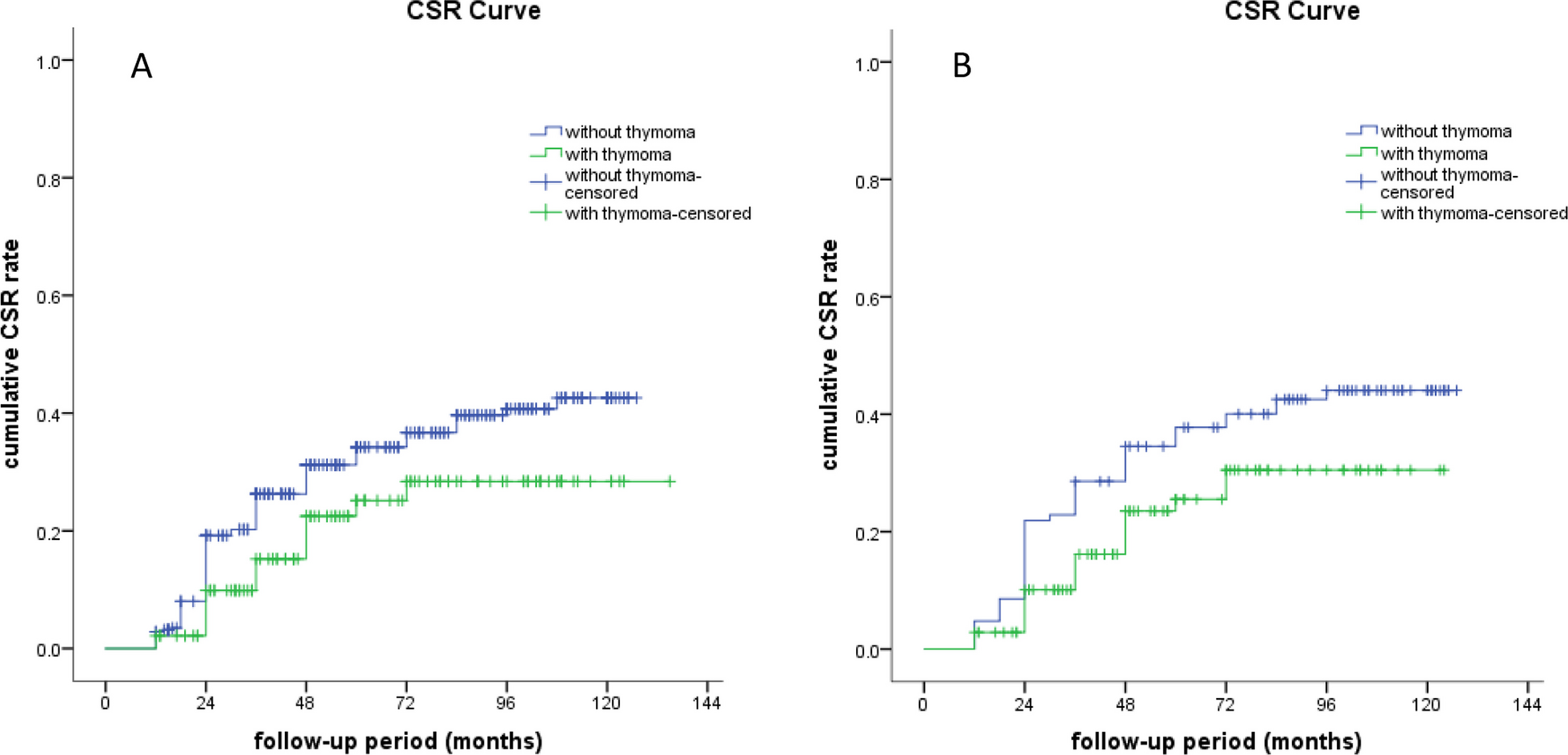
Thymoma Negatively Affects the Neurological Outcome of Myasthenia Gravis After Thymectomy: a Propensity Score Matching Study
Source : https://cardiothoracicsurgery.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13019-024-02511-6
Thymoma and myasthenia gravis (MG) interact with each other. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of thymoma on neurological outcome of MG patients after thymectomy using the propensity score...
Older patients with myasthenia gravis and a preoperative course of >1 year had a lower probability of achieving complete stable remission.

Retrospective Review of Patients With Myasthenia Gravis Switched From Plasma Exchange Therapy to Efgartigimod Treatment
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38284651/
In this series, efgartigimod appeared effective and well tolerated in patients switched from TPE.
After receiving efgartigimod infusions, 5 of 7 patients demonstrated improvement in Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America–postintervention status.

Correlation of Fatigue on Walking Ability in Myasthenia Gravis Patients: a Cross-Sectional Study
Source : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10783269/
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a neuromuscular junction autoimmune disease characterised of intermittent muscle weakness that increases with activity and recovers with rest.Analysing the correlation of fatigue on walking ability in...
There is no significant correlation between fatigue and walking ability, including comfortable walking speed, maximal walking speed, and natural cadence.

Evaluation of Medication Exposure on Exacerbation of Disease in Patients With Myasthenia Gravis
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38235027/
Of the medications reported to potentially worsen MG, intravenous labetalol and intravenous magnesium were the 2 agents associated with myasthenic exacerbations with a higher incidence in patients harboring additional risk...
Of the medications reported to potentially worsen MG, intravenous labetalol and intravenous magnesium were the 2 agents associated with myasthenic exacerbations with a higher incidence in patients harboring additional risk factors.

Safety and Efficacy of Nipocalimab in Patients With Generalized Myasthenia Gravis
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38165333/
This study provides Class I evidence that for patients with gMG, nipocalimab was well-tolerated, and it did not significantly improve MG-ADL at any individual dose but demonstrated a significant dose...
Nipocalimab was generally safe, well tolerated, and showed evidence of dose-dependent reduction in MG-ADL scores after nearly 2 months in this phase 2 study.

